5 practical ways to optimize your maintenance operations

The cornerstone of modern maintenance may be predictive maintenance, but preventive maintenance is still very much in use, especially in industries where errors can be fatal. Whichever approach is used, data plays an essential part. Better use of data results in organisations being able to determine the state of the process and condition of equipment in order to estimate when maintenance should be performed. The goal? Fix potential defects before they result in failure or effect on process performance.
On-time maintenance is made possible by the integration of data utilization capabilities. At the end of the day, successful implementation is dependent not only on the organisation’s ability to turn data into accurate information, but also to further leverage the information to implement an efficient, scalable maintenance plan. Below are some tips, tricks and first-hand examples of how you can implement new data-driven strategies to enhance productivity, profitability and efficiency gains.
Leverage modern data analytics tools
Modern software tools can help you and your team analyze available data and translate it into accurate information that will help improve operations. They combine online data from various sources, including maintenance, condition monitoring, process control (DCS) and quality control (QCS) systems, to enable efficient data analysis. The data utilization can be visual, smooth and powerful, leading to enhanced production and easier maintenance development.
For companies pointed in this direction, the best case scenario is that all digital information is seamlessly integrated and users have a clear, overall picture of the process as a basis for better decision-making.
Five practical examples of data-driven maintenance
As you review these examples, keep in mind that the opportunities are limitless when high-quality data is combined with intelligent calculations and algorithms. For example, it is possible to estimate optimal maintenance timings, calculate sub-process performances or assess runnability risks.
#1: Begin with an equipment-level view
Often, when assessing the need for maintenance, it is worth going back to basics and begin by visualizing the data. Take a pump, for example. Collect and monitor the most critical measurements regarding the equipment’s operating condition (speed, current, vibration, temperature, etc.). Learn from that if the equipment behavior is normal.
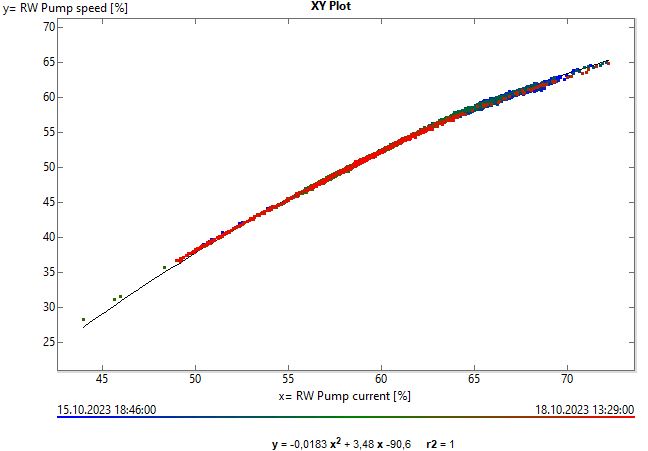
#2: Start recognizing patterns
Study the dynamics of the process. You may notice that the relationship between, for example, the pump’s speed and current follows a certain curve. A deviation from that should potentially lead to an action by maintenance.
#3: Implement an SPC approach
The Statistical Process Control (SPC) data processing method has proven its power in several process industry areas. SPC is often used within Six Sigma initiatives to provide a factual base for the measurement type of methodology of process improvement, whether such a process is in relation to a production process or a service process.
SPC limits are also regularly utilized by maintenance teams. Deviation from the limits should potentially trigger an event-driven maintenance action.
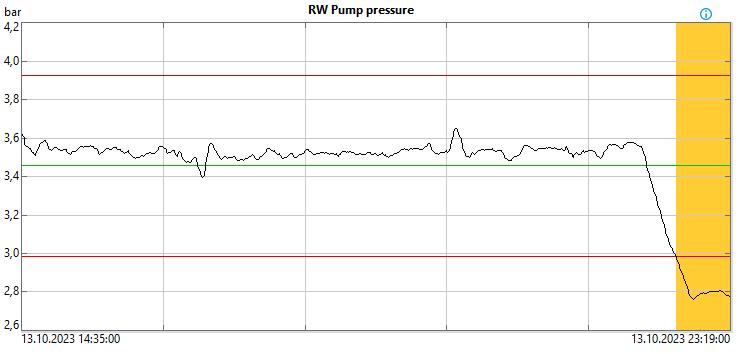
#4: Compare process condition changes
Process conditions such as equipment setup, process control strategy, used raw materials and required properties of the final product are constantly changing. Studying the process changes provides a great way to learn about the process. On Trimble’s Wedge, for example, this can be done with the annotations or notifications to contextualize data.
The maintenance team might want to compare process variables before and after maintenance activities such as pump or valve replacement. For example, what changed in the data when we replaced a pump, and what can we learn from that? Is it possible to use this new information to schedule the next pump change more accurately?
#5: Study control loop performance
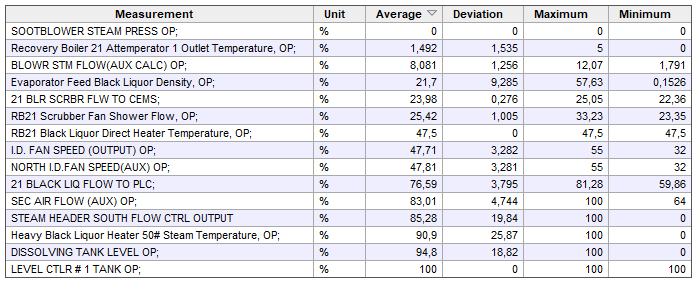
A modern production plant has a production control system and thousands of control loops that ensure production efficiency. Control loop performance is one of the automation maintenance team’s biggest headaches because poorly functioning control loops can cause serious deviations in product quality or profitability.
In order to evaluate control loop performance, combine control loop set points, controller outputs, measurements and state data. By analyzing the averages, deviations, maximums and minimums of the factors, it is possible to determine bottlenecks, dead loops, broken measurements and deviations easily.
In the end, remember that it’s not about how much data is collected, it’s what you do with the data. While most modern production operations generate significant amounts of data, the most successful ones are leveraging it to drive the business forward.
 Want more insights?
Want more insights?
Our sales team is full of data analysis experts ready to help you. Learn more about Wedge process data analysis tool.